What is BitTorrent, how does it work and what can it be used for?
What is BitTorrent?
BitTorrent is a communication protocol that allows downloading and sharing large files over the Internet without relying on the presence of a centralized server to store shared files. The protocol was designed by Bram Cohen in 2001. Today BitTorrent is one of the most popular protocols for transferring large files such as digital video and audio files.
Despite earning a bad reputation as a protocol that is used for piracy, many organizations, businesses and content creators use BitTorrent protocol for completely legitimate purposes that benefit everyone involved without breaking the law. For example, BitTorrent is used by many large and small companies for distributing software, games, videos, music and large data sets across countless users and servers.
How does it work?
Let’s look at how the BitTorrent protocol works using an example.
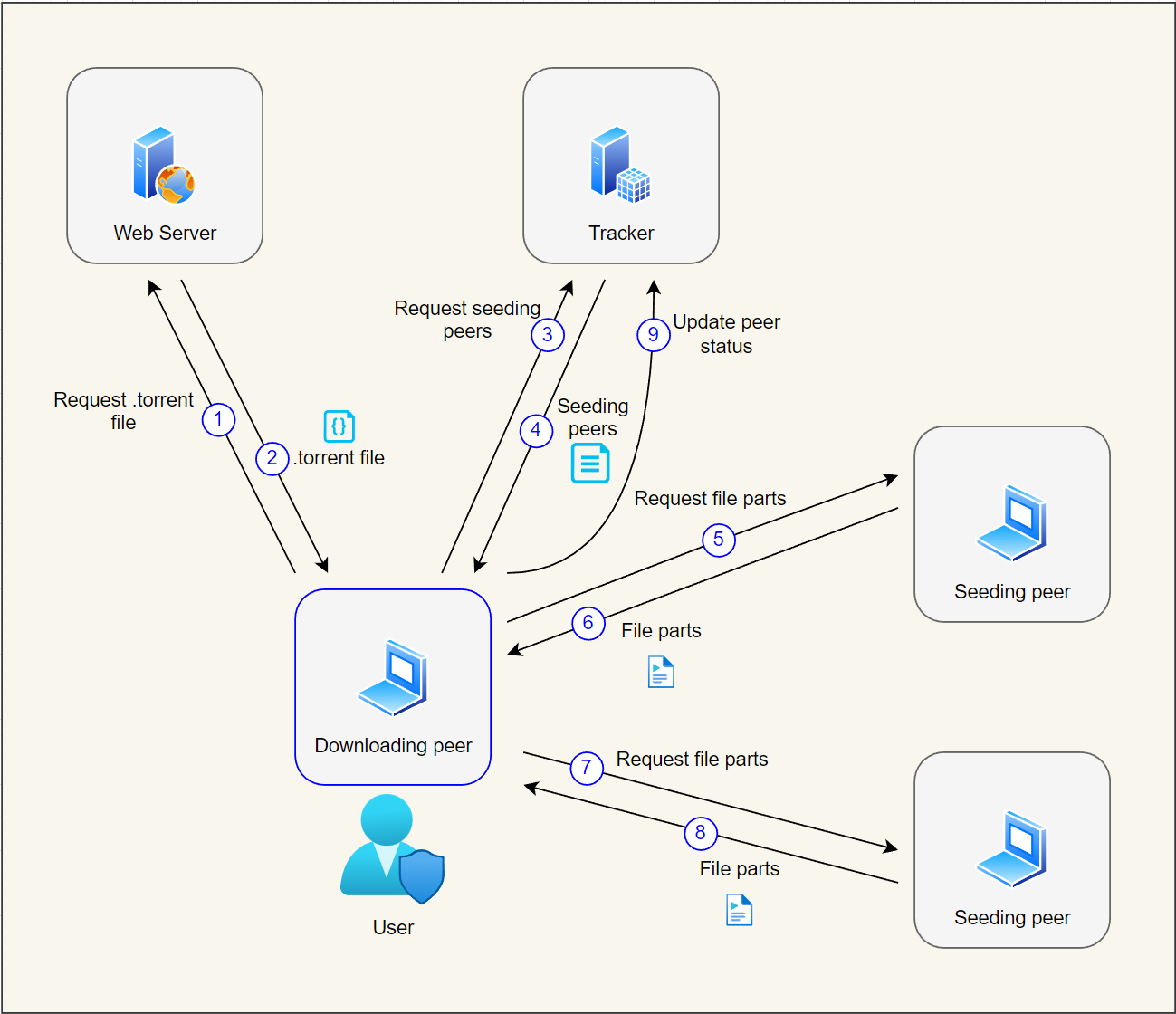 When a user wants to download a certain file or a set of files, he locates a corresponding torrent file on an index website and downloads it using HTTP or HTTPS protocol (steps 1-2).
A torrent file contains information about files included in a torrent and the address of a tracker.
When a user wants to download a certain file or a set of files, he locates a corresponding torrent file on an index website and downloads it using HTTP or HTTPS protocol (steps 1-2).
A torrent file contains information about files included in a torrent and the address of a tracker.
After downloading, the user opens the file using a BitTorrent client. The client extracts the address of a tracker from the file and retrieves the list of seeding peers from the tracker (steps 3-4). The tracker is another web server that is responsible for maintaining a list of active peers.
Next, the client connects directly to a seeding peer (step 5) and downloads parts of files included in the torrent (step 6). The connection is established using a binary protocol that operates over TCP and UDP and supports optional encryption. If multiple seeding peers are available, the client will be able to download files faster by simultaneously downloading different parts of files from different seeding peers (steps 7-8). Seeding peers are just other computers that run a BitTorrent client and already have the required files.
After downloading parts of the files included in the torrent, the client reports the status to the tracker (step 9). This step allows other peers to start downloading files from this client.
Once all parts of all files are downloaded to the client, the download completes and the client remains available so that other peers can use it for downloading files available on this client.
It is important to note that BitTorrent protocol does not have built-in security, privacy, and anonymity features. Connections between a tracker and a client can be encrypted using industry-standard HTTPS protocol and connections between peers can be encrypted using a weak encryption algorithm. However, ISPs can identify BitTorrent traffic while other peers can determine which files are shared by a particular peer. Also, files that are shared using BitTorrent protocol may contain malware which puts at risk users of public BitTorrent networks.
What is it good for?
Despite its security and privacy shortcomings, BitTorrent is a mature protocol that can be used for applications ranging from file-sharing to content distribution to backup and synchronization. Its decentralized and peer-to-peer nature allows for fast and reliable distribution of large files, making it a popular choice for many users and organizations.
Have a question or suggestion?
There is more than one way to start a conversation:
Create a post in our Reddit community.
Fill out the form.
Send us an email: info@relbis.com